Microservices Design
After identifying the application requirements and the main components of the architecture, in this section, the microservices design of the system is defined.
Each service is responsible for a specific set of features and communicates with other services through well-defined APIs. This allows to develop and deploy each service independently, enhancing scalability.
Furthermore, the decomposition of the system in microservices allows the project to be easily extended, maintained, and tested.
API Design
Each microservice either exposes a REST or WebSocket API for communication with other services. The APIs are designed to be simple, consistent, and easy to use.
The APIs are versioned to ensure backward compatibility and to allow future changes to be made without breaking existing clients.
The APIs are documented using either OpenAPI (formerly known as Swagger) or Async API to provide a clear and comprehensive reference for developers who want to integrate with the system.
Auth Service
The Auth service exposes a REST API for user authentication. It provides endpoints for user registration, login, and logout.
Feature: Authentication
Feature: Authentication
As a user
I want to be able to authenticate with the system
So that I can access my account
Scenario: User registration
Given I want to register
When I provide a valid registration data
Then I should be registered successfully
Scenario: User login
Given I am a registered user
When I provide a valid login credentials
Then I should be logged in successfully
Scenario: User logout
Given I am a logged-in user
When I log out
Then I should be logged out successfully
Profile Service
The Profile service exposes a REST API for managing user profiles. It provides endpoints for viewing and modifying user information.
Feature: Profile
Feature: Profile
As a user
I want to be able to view and edit my profile
So that I can update my information
Scenario: View profile
Given I am a logged-in user
When I request to view a user profile
Then The user profile should be returned
Scenario: Edit profile
Given I am a logged-in user
When I update my profile information
Then My user profile should be updated
Session Service
The Session service exposes a WebSocket API for managing sessions. It provides endpoints for creating, joining, and leaving sessions. It also handles video playback synchronization and chat functionalities.
Feature: Session
Feature: Session
As a user
I want to be able to create and join a streaming session
So that I can interact with the Youtube video and the chat
Scenario: Create a Session
Given I am a user logged-in
When I create a streaming Session by providing a correct Youtube URL
Then I should receive the Session name
Scenario: Join a Session
Given I am a user logged-in
When I join a streaming Session by providing a correct Session name
Then I should receive the Youtube video Id
Scenario: Leave a Session
Given I am logged-in user and I am joined in a Session
When I leave the Session
Then I should be successfully disconnected from the Session
Scenario: Play/stop/move the timeline of a Session Video
Given I am logged-in user and I am joined in a Session
When I play/stop/move the timeline of the Session Video
Then I should receive a Video State as a synchronization message
Scenario: Join a Session
Given I am a user logged-in
When I join a streaming Session by providing a correct Session name
Then I should receive the Youtube video Id
Clean Architecture
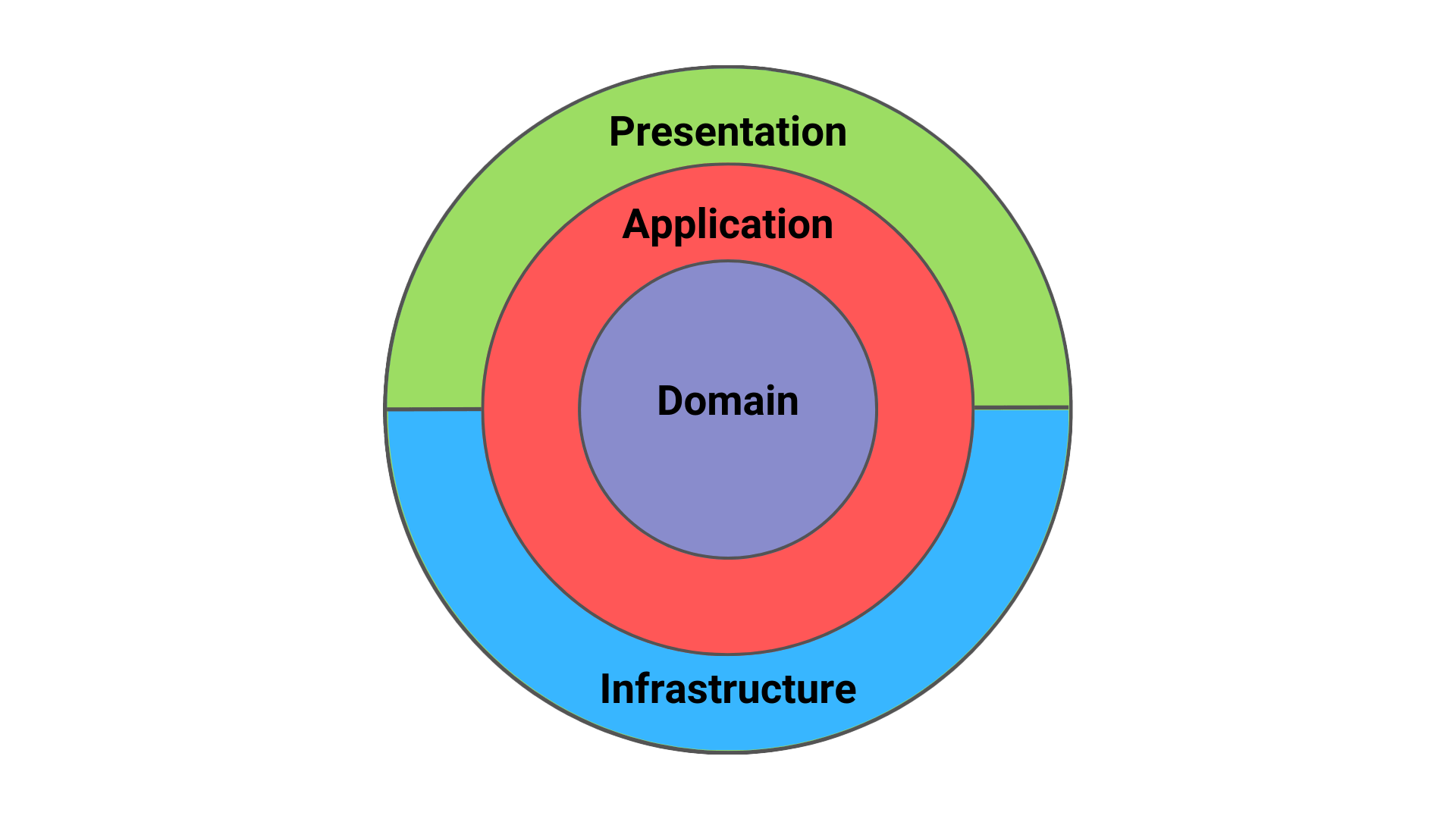
The design of all the microservices follow the Clean Architecture. This architecture allows to separate the domain from the technical details. The architecture is composed of multiple layers and is based on the Dependency Rule, i.e. each layer can only depend on the inner layers. The adopted layers are the following:
- Domain. It's the innermost layer and should contain the business logic of the microservice. It comprises DDD aggregates, value objects, entities, factories and repositories;
- Application. Should contain services;
- Presentation. Should handle data serialization/deserialization for sending/receiving data with other microservices;
- Infrastructure. Should manage the communication with the external microservices.